Written By, Dr. Annjaan Daash
1 Training and Placement Head, Regional College of Management, Bhubaneswar, Odisha; Research Scholar at Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar, T.N., India
Abstract:
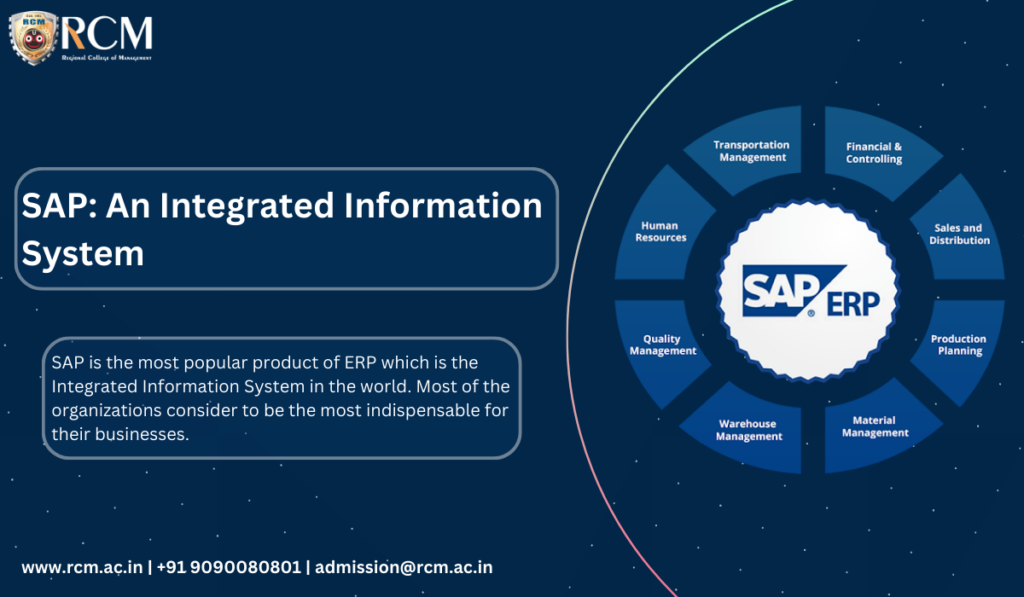
SAP is the most popular product of ERP which is the Integrated Information System in the world. Most organizations consider it to be the most indispensable for their businesses. The SAP software has various technical and functional modules across the department functions that can be shared in real-time data processing. By doing so there is participation between various departments across the organizations towards achieving organizational goals faster. SAP is flexible, stretchable, and can adapt to any system of the organization to attain its objectives.
SAP is widely used in more than 180 countries having 4,25,000 customers and is part of the EuroStoxx 50 stock market index. SAP ERP is an integrated system where there are continuous interactions and there are no data discrepancies between any subsystems. SAP is an enabler that improves business processes to enhance output and insights and thereby align the policies and operations of an organization.
Keywords: SAP, Integrated Information System.
1. Introduction
IT (Information Technology is a term that encloses all forms of technology used for the creation, storing, and exchanging of information in its various forms. Various forms can be business data, voice conversation, and motion pictures. It is a technology that is propelling which is commonly known as the “information revolution”.
Information technology (IT) is the utilization of computers and telecommunications equipment to store, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data. Several industries are associated with information technology, such as computer hardware, software, electronics, semiconductors, internet, telecom equipment, e-commerce, and computer services. In a business context, the Information Technology Association of America has defined information technology as “the study, design, development, application, implementation, support or management of computer-based information systems”.
In today’s world, the way we live & work is dominated by IT. IT has given us the ability to use information the way we want. Information can be of high precision, efficient transmission & manipulation. Business today has become competitive & to maintain this competitive advantage quick business decision has to be taken. For quick decision making the information has to be managed by automating the process of data collection. IT is essential at organizational level in assisting its objectives & strategies. At the departmental level, IT ensures a smooth flow of information across the department. IT does this by developing and maintaining an enterprise-wide database that is accessible across the department boundaries.
2. Evolution of ERP
The evolution of ERP has been etched back to the 1960s. During that period the core focus was mainly on inventory control. When the computer was economical, the calculation of the salary of employees was a repetitive function, the next thing for calculation for manufacturing companies was the number of materials they needed to buy for which companies purchased different applications which were quite highly-priced.
In 1970 the locus was directed toward MRP (Material Requirement Planning).MRPI helped in translating the master production schedule into requirements for individual units like sub-assemblies, components, and other raw material planning & procurement. This system looked into the planning of the raw material requirements.
MRP was first developed by IBM known as IBM RPS (Requirements Planning Systems).
• Drawback of MRP :
- Every MRP run produced widely different results because of change in demand & supply.
- The systems had the effect of raising the inventory instead of reducing. The reason for this was for every fluctuation upwards increased supply orders that could not be easily reduced.
- This resulted in over piling of stocks, over supply and storage problem and loss of materials.
The early planning systems could not be trusted & in early 1970s the concept of master production scheduling & capacity requirement planning were introduced into MRP I to overcome the consistency& inventory problems.
In 1980s the concepts of MRP II (Manufacturing Resource Planning) which involved enhancementof the entire plant production was introduced.
Reasons for MRP failures:
Most of the vendors did not comprehend master scheduling, so they motivated the companies to implement MRP II packages in old MRP Iprocess, that is without proper usage of master scheduling & capacity planning.
Inaccurate data:Every time the MRP II was run it produced inaccurate inventory records & bills of materials.
Needs of business was not addressed: Software resulted in lot of cost but no business benefits.
The planning system requires business manager to understand its principles. As the software was very expensive so the financial objectives of the organization were not met.
Insufficient education to the managers of how to use the software. There was no training provided adequately on each module to all the users.At least 3 whole days of software training to the employees is required.
Ineffective use of Consultant: Several organizations try to execute the system without the help of consultant who have vast experience in this field before.
3. Enterprise Resource Planning
ERP was introduced to overcome the problems faced by MRP II but in practice, ERP is just MRP II with some special features.
- Enterprise: Entity
- Resource: Man, Money & Material
- Planning: Optimisation of resources
Source: Gartner’s Research Note SPA-12-0420)
Definition : Enterprise Resource Planning is a software solution that integrates internal & external management information across an entire organisation which includes Finance, Sales, Manufacturing, HR. ERP optimises all business processes
ERP is a software driven business management system, which integrates all facets of business including planning, manufacturing, sales, marketing.
The market scenario has changed from local to global. So companies has to improve competitiveness by lowering operating cost & improving logistics.
Detailed Definition
“a business strategy and set of industry-domain-specific applications that build customer and shareholder communities value network system by enabling and optimising enterprise and inter- enterprise collaborative operational and financial processes” (Source: Gartner’s Research Note SPA- 12-0420)
ERP is a software solution that takes care of organisation needs by integrating all the functions to get the best out of the company. ERP is a concept which has developed SAP. SAP is a product of ERP Packages of ERP :
- SAP
- Oracle
- SQL
4. SAP: System Application & Products used in data processing
SAP is a company in Germany founded by five ex-IBM engineers. SAP stands for Systeme, Andwendungen, Produkte in der Datenverarbeitung which can be translated to English meaning Systems, Applications & Products in Data Processing. These people studied various sectors in the industries & understood the business processes & built an Integrated Information System which was popularly known as SAP. SAP is integrated business suite that is designed to handle data processing. SAP was developed with a perception of creating a standard application software for real-time business processing. SAP stands for Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing. Since its origin SAP has issued various advanced releases, such as SAP R/1, SAP R/2, and SAP
R/3architecture . The R in this architecture stands for “Real-Time” data processing. The 3 in the R/3 stands for three-tier client-server architecture. The latest release of SAP is SAP Business Suite 7.
Source: https://www.oreilly.com/library/
Table 1-1 lists the major SAP releases and the release year.
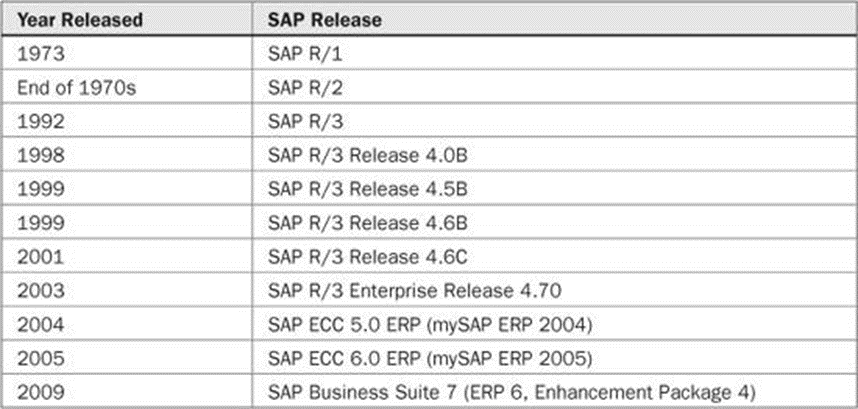
TABLE 1-1 Major SAP Releases
History of SAP Company – Timeline and Infographics
| YEAR | PRODUCT/RELEASES | CUSTOMERS |
| 1970 | SAP R/1 | 40 |
| 1980 | SAP R/2 | 2,200 |
| 1990 | SAP R/3 | 15,000 |
| 2003 | My SAP | 41,000 |
| 2005 | SAP ERP | 1,00000 |
| 2010 | SAP Business One | 2,50000 |
| 2016 | SAP S/4 Hana | Global Presence in 188 Countries |
| 2018 | SAPS/4 Hana updates + security patches | 46 years of success |
Source: https://www.sap.com/corporate/en/company.fast-facts.html#fast-facts https://www.sap.com/corporate/en/company/history.html http://www.sap.com/corporate-en/factsheet
5. SAP R/3 CLIENT-SERVER ARCHITECHTURE:
SAP is an integrated system that operates at real time. It means information gets automatically updated in all department. Initial release of SAP was called R/2 on a mainframe a financial package. 70% of fortune 100 companies are using SAP. (Gartner research 2008). 70% of all the fortune 100 companies (according to Gartner research 2008) uses SAP. Also, according to Gartner research 2008, 50% of all the fortune 500 companies uses SAP. Huge companies like Google, Microsoft, Apple,3M, Johnson and Johnson, Deloitte, PepsiCo etc will use SAP.
For Small & medium enterprises SMEs with turnover of 100-700 mn SAP has released Business One & By Design (Hosted/ customized version of SAP). Business one is Stand Alone Version,Independent Silos of SAP which individually deal with certain problems of a particular function.
SAP R/1 :- In R/1 architecture where R stands for real time processing of data, all the three layers that is Presentation, Application and the Database were located in 1 system / server.
(one layer: Presentation + Application + Database)
SAP R/2 :- In 1979 second version of SAP R/2 was released. with IBM’s database and a dialogue- oriented business application. In R/2 architecture all the three layers that is Presentation, Application and the Database were installed in 2 different servers.
(Server one: Presentation, Server two: Application + Database)
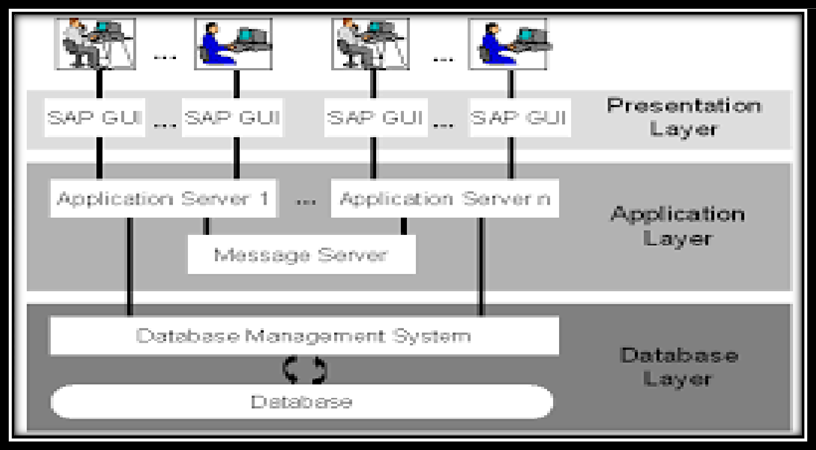
SAP R/3 :- SAP upgraded R/2 to R/3. SAP R/3 is the client/server architecture , it is 3 tier architecture where three layers Presentation, Application and data base are installed in three different server/system.
(Server one: Presentation, Server Two: Application, Server Three – Database)
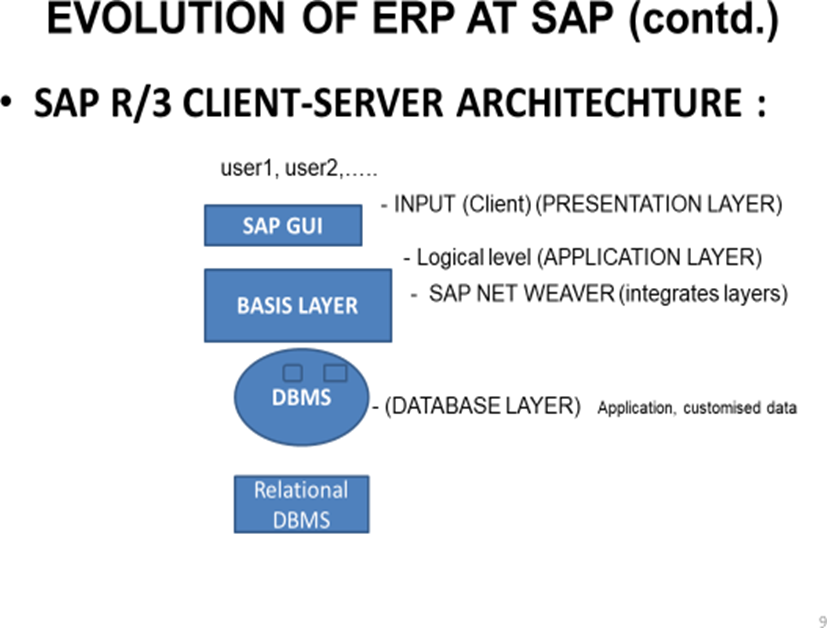
SAP NETWEAVER ARCHITECHTURE:
SAP R/3 client server architecture information gets updated at real time as there is real time data processing, It is also known as SAP Business suite.
SAP LAYERS:
1. Presentation Layer:
It accepts inputs from function keys given by the users. It is also known as Input Layer or the Client layer. SAP GUI is presentation layer; this window is SAP GUI which deals with interaction between PC & users. Presentation layer is installed in user’s desktop . When it is run it displays R/3 menu in the window.
2. Application Layer:
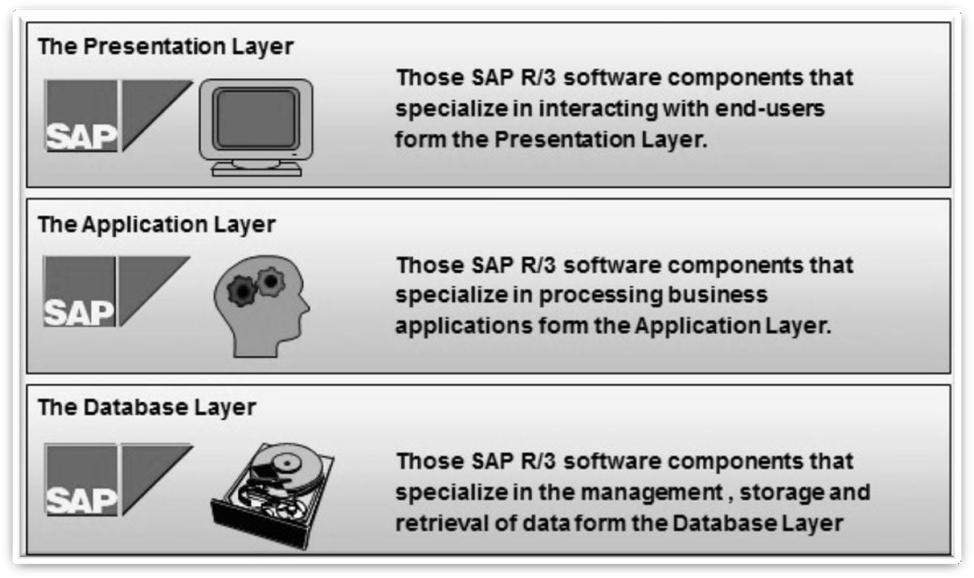
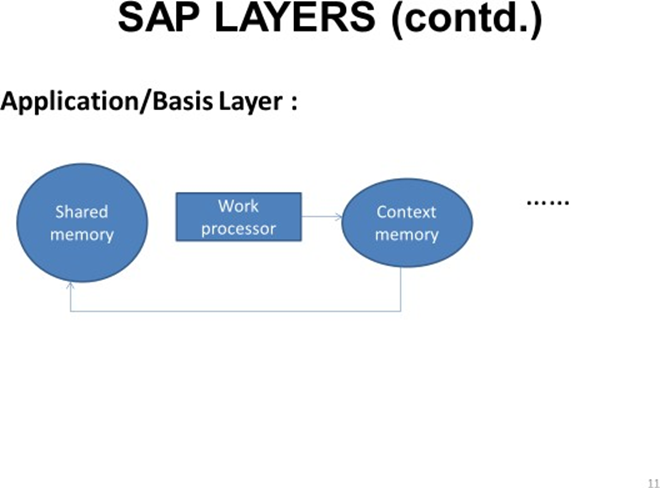
Application Layer is also known as Basis Layer or ABAP layer. It is a logical level where Processing & Execution of programs takes place. There is conversion from source code to Application layer. It Contains set of work processor & message server. The message server finds which work processor is free & then directs all the inputs to those free work processors. This is known as Current Load Balancing. These work processors contains context memory & shared memory
Dispatcher: It is in message server. It deals with distribution of transaction load into free work processor. It acts as a link between users & work processor.
Message Server: It contains dispatcher which checks the work processor which is free & allots load to that work processor. Work processor is a place calculation & execution of programs takes place. Current Load Balancing: Process of allotting loads to free work processor. A work processor works on a particular input and the result is stored in context memory then it is transferred shared memory.
3. Database Layer:
It fetches data from RDBMS. Consists of application & customised data.
Respiratory: It is a Area where programs are stored. A total of 6 sessions can be carried out in SAP. The output data of entire R/3 architecture is stored in RDBMS.
The Database layer comprises of 2 major components. It consists of DBMS and R-DBMS. The SAP has developed its own database called as Hana which is adaptable with all major databases such as Oracle.
6. Key Characteristics of ERP SAP
1. Integration:
ERP SAP expedites organization wide integrated information system which covers most of functional areas like Sales, Finance, HR and Manufacturing. SAP is a combination of various modules which are integrated into a single system. It Performs core activities & increases customer service as these modules communicate with each other that helps in quick decision making. It bridges information gaps across organization. Unique reports that are required by the clients which is also called as customized reports, So technical consultant modifies the reports and fills the gap. It facilitates better project management. It allows automatic introduction of technologies : internet, intranet, video conferencing, e-commerce. It facilitates productivity enhancement, cash management, inventory problems, prompt delivery. SAP is integrated information system modules of business configuration. There was a report from Hejazi etc. in 2003. They also point out that SAP could more effectively integrate various resources during they pay more attention on working SAP (Hejazi etc., 2003). In addition, in 2002, Mandal and Gunasekaran all argued that the organization of SAP owned whole view of the process. This structure could help enterprise effectively manage enterprise-wide project. Therefore, it is confirmed that SAP could help enterprise improve efficiency of integrating resource.
Source: Hejazi, S. S., Halpin, A. L., & Biggs, W. D. (2003).
2. Packages:
ERP-SAP system cannot be developed inhouse but by vendors. If the organization wants to implement ERP – SAP it is done by consultants. We need to map organizational business processes with the jargons employed by vendors. So organizations enter into long term relationships with the consultants.
3. Best Practices:
ERP consultants are in dialogue with different with various organizations of a given industry and with various academicians to figure out the most effective way of taking care of business processes. The result is claimed to be “industry best practices”. Any change in the business processes will affect ERP implementation. So organizations do not accept such practice. If there is a change in business process , ERP SAP should be modified as per the new business processes. So it involves cost which organization are resistant to change.
4. PC Assembly:
While installing ERP SAP the software gets integrated and not the platform on which it operates. Most companies face difficulties in integrating their ERP-SAP with their package of hardware, operating systems, database management systems software, and telecommunications suited to their specific needs.
5. Evolving:
Enterprise Systems are changing rapidly. Architecturally: Mainframe, Client/Server, Web-enabled, Object-oriented, Componentization.
6.
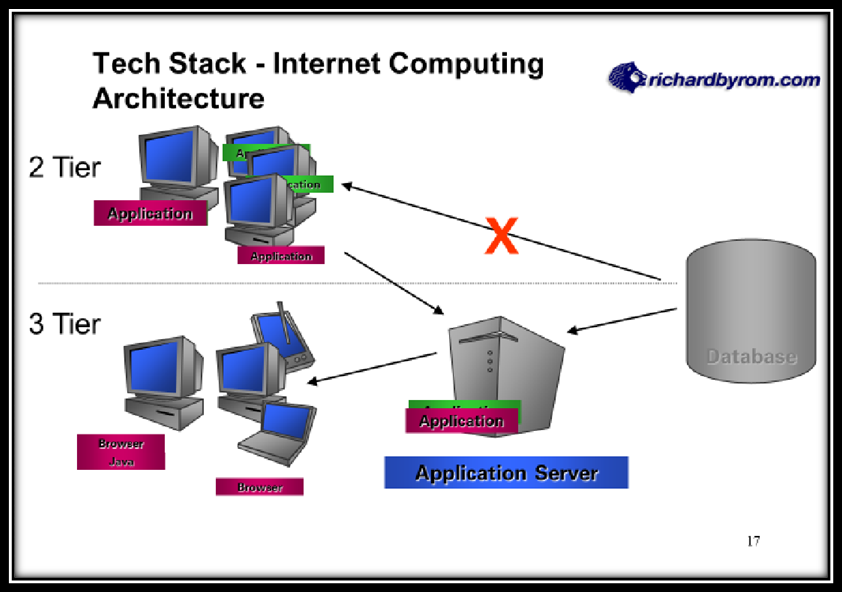
There is an interaction between MAN – NACHINE and his software program. It is Integrated- Multi- tired Architecture which is flexible in nature. We have moved from two tier to three tier architecture. In any client-server architecture when the number of users becomes large then that many times we have to load the application that many times, but in R/3 architecture repeated installation can be avoided as the application is stored in middle tier. The new application gets downloaded automatically.
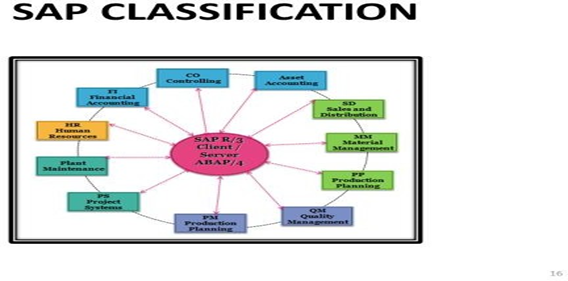
7. SAP – HR:
PERSONNEL STRUCTURE :
- Employee Group & Sub group :
- Active Employee : Employees who has relationship with company
- Ex. : Permanent, Contractual, Trainee
- Inactive Employee : Employees who has no relationship with company
- Ex. : Resigned, Terminated, Retired.
INFOTYPES: They are units of information in the Human Resource Management System.
- It is a logical set of records
- Ex : IT 0006 : Address 0002 : Personnel Data
0008 : Basic Pay 0009 : Bank
000 : Administrator 001 : Reference client
006 : Early watch client
8. BENEFITS OF SAP:
1. Better Corporate Governance:
Rules, process, towards which company is directed. Once SAP is used in the company it helps achieve organisation objective as there is real time data processing across all organisation.
2. Reduced Cost:
As SAP integrates all business process into the system where there is real time data updation. All the information are there in the system. So it reduces number of employees required to do the job.
3. Increased effectiveness & efficiency of business:
The productivity enhancement arising from SAP is tremendous. Data’s is entered only once. Data’s entered can be forwarded to other employees my email. For ex.: Emp leave application form submission, approval by HOD, leave balance can all be done by SAP.
4. Employee empowerment:
Encourage employees to participate in decision making process. It is a way to motivate the employees. If there is a web portal in SAP, organisation can streamline the process, reducing cost. (paper based process).So an empowered employee works on latest technology rather than paper based work.
5. Makes organisation flexible & less rigid structure:
Organisation becomes transparent as data’s are integrated into the system & changes in the data are done in real time.
9. REFERENCE:
- Gartner, Forecast: Enterprise Software Markets, Worldwide, 2008-2015. Gartner Group, 2011.
- Hejazi, S. S., Halpin, A. L., & Biggs, W. D. (2003). Using SAP ERP technology to integrate the undergraduate business curriculum. Developments in Business Simulation and Experiential Learning, (30), 122-125.
- Mandal P. and Gunasekaran A. (April, 2002). Issues in implementing ERP: A case study.
- https://www.sap.com/corporate/en/company.fast-facts.html#fast-facts
- https://www.sap.com/corporate/en/company/history.html
- http://www.sap.com/corporate-en/factsheet
ANNEXURE
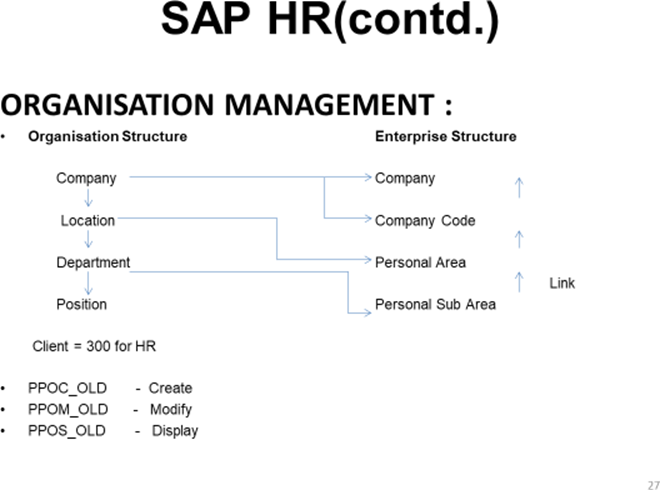
ORGANISATION MANAGEMENT
Source: Based on the authors work done at CDAC, NOIDA 2013
1. PPOC_OLD

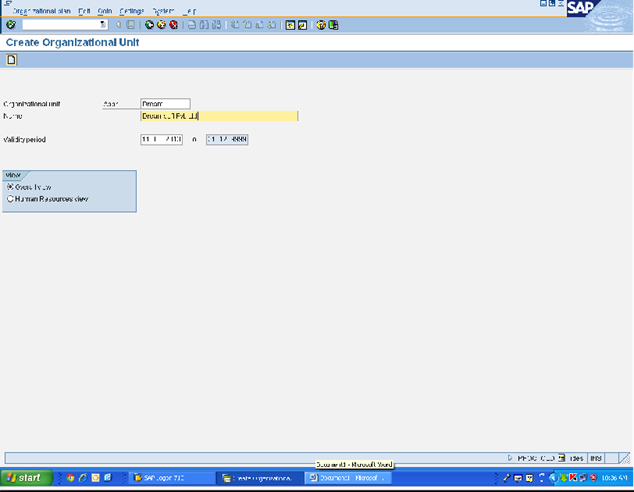
Press enter
2. PPOM_OLD
Click on the company name, create (F7): white color create button
Create the location and save
Create the location and save
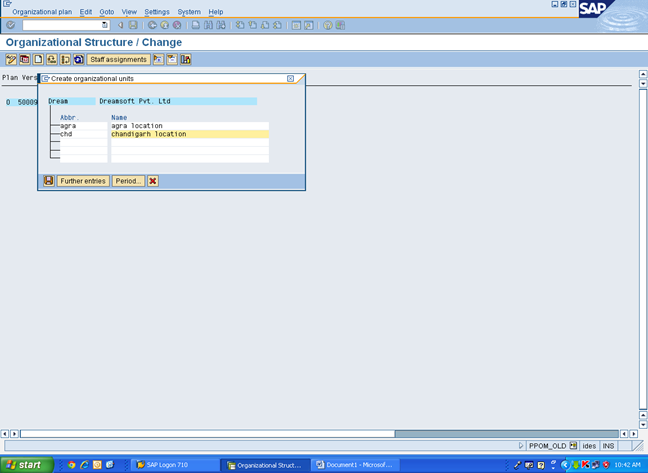
3. Create Department: Click on Agra– create F7
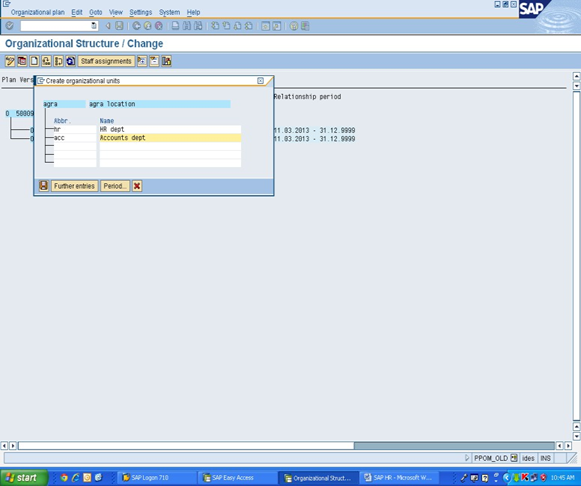
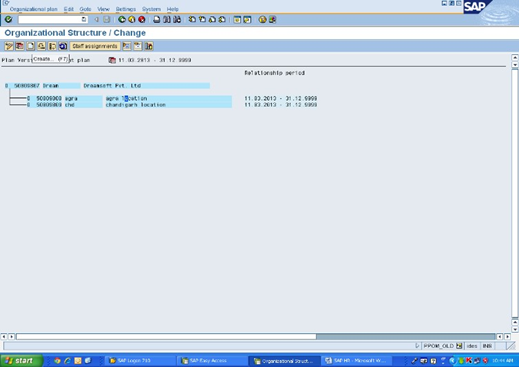
Same for Chandigarh lcocn