Written By, Annjaan Daash || Dr. Prabir Pal || Dr. S. Pragadeeswaran
Abstract
Leadership versus Leaders are both sides of a coin as both matters. The cynosure is the leader and embraces the qualities of the individual and how they lead and involve others. A leader pinpoints competencies like knowledge, skills, and abilities and shows a clear path to the individuals so that they are adept in potentiality and are able to manage others.
Emphasizing leadership highlights the caliber of leaders within an organization, not merely an individual leader but the entire system and the processes that generate these leaders. Outstanding leaders might appear and exit but the tide of leadership remains forever.
Genuine leadership doesn’t deal with a single person but also it takes into account the entire process. We can appreciate and gain knowledge from any person who is an impressive or excellent leader. The final outcome of an organization’s leadership robustness is obtained by building a leadership pipeline that entrusts stakeholders’ confidence in achieving future results.
Leadership focuses on an individual whereas building leadership emphasizes the organization that generates leaders. Leadership brand is the identity of the leaders throughout the organization that bridges customer expectations, and employee and organizational behavior. (Ulrich et al, 2007).
Leadership necessitates the opinion about the X factor or the systems and processes that raise the next generation of leaders who will respond to future customer and investor assurance. Branding Leadership also helps in building the next generation of leaders. Firms with leadership brands have an eternal and durable reputation.
When the organization’s brand interwinds with its leadership brand, the former sustains and outlives any single individual leader.
Keywords— Leadership Brand, Competencies, Leadership Development.
1. INTRODUCTION
The World of HR Today
The main function of HR is to add value to become the root of competitive advantage. When HR converges on generating talent acquisition and building firm capability which connects to customers to have a competitive advantage. It has the capacity to be elemental to major business outcomes: market share, revenue growth, profitability, and sustainability.
Objective of HR
There are six noteworthy objectives by which customer-focused HR adds value toward increasing an organization’s business.
Competencies – The CORE 6
1. A Master Thinker
- Annjaan Daash, Training and Placement Head, Regional College of Management, Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
- Research Scholar at Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar, T.N., India.
- Dr. Prabir Pal, Prof., Chairman, Regional College of Management, Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
- Dr. S. Pragadeeswaran, Professor, Department of Business Administration, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar, T.N., India.
2. An Energetic Leader who Initiate, Execute, Influences, and Inspire
3. A Great Communicator and a Skilled Builder of Relationships and Networks
4. A Wonderful Team player
5. A Live Example of Deciding, Acting, Delivering, and Staying Fast
6. A Lifelong Learner with High Technical Expertise
Master Thinkers in the Organization, HR professionals should take the lead in addressing manpower and organizational issues.
Line managers propose that HR is more of an internal police function and that HR professionals act as process facilitators or transactional administrators and focus more on internal HR matters rather than critical business issues. However, it is proposed that they should be the highbrowed architects designing talent acquisition and organization agendas for their firms.
Leaders, along with HR professionals, must be equal associates with line managers to accomplish the organization’s objectives.
Take for example, if a CEO suggests that the organization would proceed in a particular direction while the rewards and remuneration system recognizes employees for going in another direction then there is a detachment so the impact of leaders along with collaborative HR practices will nullify each other and competition wins. Thus it is emergent that HR and line leaders be hitched together and headed in accomplishing the organization’s objectives.
HR Should be a Team Player and Contribute Substantially Towards Revenue Growth
When there is no demand for the product, its benefit is zero no matter how much of it is manufactured. Therefore, HR professionals must have a beeline to the outside customers. HR from Outside-In means the HR professionals need to partner with the business and if the clients of the business are the outside customer then HR’s line of vision through teamwork must run outside-in.
A great communicator, HR should create and sustain economic assets that are appraised and remunerated by capital markets.
- Pledging by delivering compatible and predictable results
- Developing an eloquent and imperative strategy for the business future that motivates great communication with customers, product innovation, and spatial expansion.
- Banking upon the core competencies by identifying and providing tangible investments in different resources.
HR Needs to Decide, Act, Deliver, and Stay Fast to Get both Talent Acquisition and the Organization’s Objective on the Same Page
- Talent acquisition can be achieved by hiring the best individuals in the industry as per the requisite competencies defined by the organization to have a competitive advantage and HR should encourage employees to work as a team and decide, deliver, and act together to achieve organizational goals.
HR professionals should be Lifelong Learners of High Technical Expertise as per domain-specific, the primary source of competitive advantage and create practices that support it :
- In the pharmaceutical industry, a company needs to have high technical expertise in the chemical structure of medicines that can treat any disease. If an organization identifies something then in due course of time its competitors will probably know it as well. Does an organization have a culture that promotes creativity, innovation, learning, and technical know-how? In the era of technological stir, HR emerges as the epicenter in building competitive advantage.
II. HUMAN RESOURCE COMPETENCY STUDY
From the inception of, the Human Resource Competency Study was outlined in close association with leading academicians, practitioners, HR associations, and line managers. There were surveys done in 1987, 1992, 1997, 2002, 2007 and 2012. The research team scrutinized the relevant literature on business trends, HR Practices, and competencies. Secondly, numerous interviews were done with various professionals, line managers, academicians, and consultants in face-to-face interviews or semi-structured focused groups. 2012 research advances the global range of the study by including the leading HR professional organization in Australia (AHRI), China (51 jobs), India (NHRD), Latin America (IAE), and the Middle East (ASHRM). Northern Europe (HR Norge), South Africa (IPM) and Turkey (SCP).
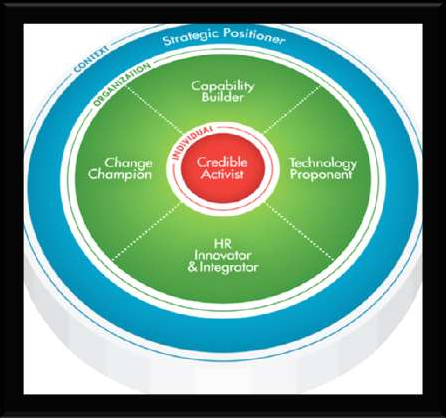
Source: Ulrich et al 2013.
Overview of 2012 Findings
Six domains of HR competencies were identified and represented below figure, (Dave Ulrich et all 2013, Global HR competencies)
1. Credible Activist
In high performance organization HR acts as credible activists. They are strong skilled builder of relationships which helps in establishing good rapport with key stakeholders and contribute towards business results.
2. Strategic Positioner
High-grade HR professionals assimilate the global business scenario – the social, political, economic, environmental, technological, and demographic trends that support the business. They are actively involved in expanding customer-focused business strategies and elucidating business strategies to attain goals.
3. Capability Builder
Capability represents what the firm is good at and known for. It embraces innovation, speed, customer focus, efficiency, and the conception of the meaning and plan of work. HR professionals engage the team members in a dialogue about their hopes, dreams, and aspirations so that they can inspire a shared vision which is communicated to all.
4. Change Champion
Efficient HR professionals promote their organization’s capabilities to revolutionize and then transcribe that into effective change processes and structures that build competitive advantage.
5. HR Innovator and Integrator
In an organization, one of the key aspects of effective HR professionals is their ability to integrate HR practices around a few critical business issues.
Moreover, high-performing HR professionals with leadership qualities continuously develop unique winning capabilities for the business.
By doing so, they consistently deliver trend-setting solutions that drive both business success and employee growth.
III. DEFINING LEADERSHIP BRAND
Source: (Dave Ulrich et all 2007, Leadership Brand)

The next factor of HR innovators and integrators is the leadership brand. A leadership brand has both invisible fundamentals and visible differentiators of its own. It is the identity of the leaders throughout an organization that bridges customer expectations and employee and organizational behavior, Ulrich et al, 2007. Traditional leadership is from inside out and leadership brand is from outside in. Leaders must get the invisible basics correct and efficiently organize and deliver the fundamentals that keep their products and services at levels that meet and exceed customer expectations.
What is the Answer to the Age question of whether Leaders are Born or Bred?
Recent research puts it at fifty-fifty, that is half of a leader’s traits grow from heritage, and half are acquired from experience. An analogy to this end could be why some people wait for the organization to spoon-feed the way to serve a customer and why some people do not have to fed/remind much, to serve customers; they just do it as mere deliberation. In an organizational context, we need to define what percent of leadership code could be learned from experience and what comes from heritage. This will give us a reason to focus on what leadership behaviors to look for in recruitment and what leadership behaviors to focus on in leadership development.
After conducting a series of focused group interviews with thought leaders and esteemed colleagues, it has been estimated that the leadership code encompasses all the essential elements that define effective leadership. Consequently, the working hypothesis suggests that this code accounts for approximately 60–70 percent of what constitutes good leadership (Ulrich et al., 2007). Moreover, according to exemplary studies on leadership, the leadership code is structured around five key dimensions.
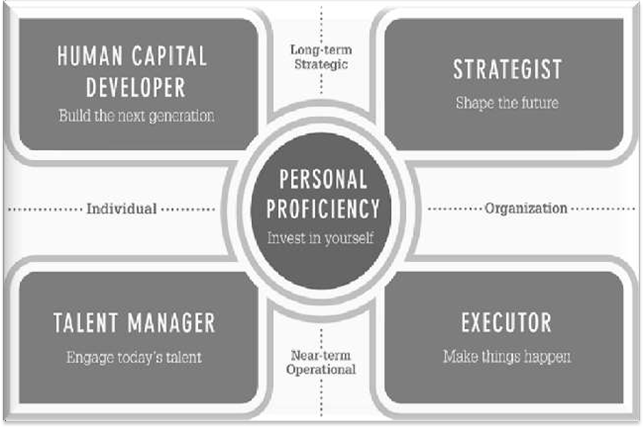
IV. MAJOR LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES
Objective
It is said that we think globally and act locally. While local patterns change more rapidly than common global patterns hence the key competency for any organization may have its significance for a considerable period but for local customization the behavioural descriptors needs to be revisited at regular interval.
In the light of above, this study aims to design a leadership training module for the senior executives of NTPC in India.
An Energetic Leader who Initiate, Execute, Influence and Inspire
Master the art of modeling the way, inspiring a shared vision, challenging the process, enabling others to act, and encouraging the heart.
1. MODEL the Way
- Having a clear sense of mission, knowing where we are headed, and seeing the end results. Doing all that builds trust and practices integrity. Being able to make a judicious decision in the absence of a clear picture, precedents, and guidelines. Going the extra mile to seize the opportunity for challenging and bigger initiatives. Being able to uncover the gifted abilities of other individuals. Strategists: Leaders need to have a point of view about the future and be able to position the firm for future customers. Displaying good peripheral vision for how to scope, scan, and interpret signals hidden in plain sight. Engaging everyone shopping for ideas, searching for the best practices as well as the “next practice” Being able to consistently invest the majority of his time in fewer areas that produce the
- greatest results.
- Knowing what causes momentum in the organization and how to keep it going.
2. INSPIRE a shared vision
Discovering a compelling common ground in every vision
- Engaging the team members in a dialogue about their hopes, dreams, and aspirations Convincingly articulating the vision of the future to the members of his team Executers: Leaders need to be able to make things happen in order to deliver results by sharing the vision with all.
- Generating buy-in of solo experts to practice the power of collective “group think”
- Communicating the common vision in an attractive, appealing way with best-selling words, imagery, and metaphors
3. CHALLENGE the process
- Asking incisive questions that open minds and incite the imagination.
- Having the courage to say no on logical grounds, even to influential and powerful people, and even if it will make them unhappy or upset.
- Challenging the status quo in the absence of a blessing or “buy-in” from key individuals in the organization
- Personal Proficiency: Make bold and courageous decisions and build trust.
- Having a great Emotional Quotient to stay on course even if fatigued or discouraged.
4. ENABLE others to Act
- Communicating an activity with a clear line of sight to business outcome
- Enlarging people’s sphere of influence and strengthening others by sharing power and discretion.
- Creating a climate for learning and always encouraging reverse mentoring.
- Human Capital Developers: Leaders need to work on their future employees to delegate and build future talent.
- Making it safe for others to experiment.
- Providing challenging and value-added stretched assignments for all of his direct reports.
- Is able to go for small and big wins together on a consistent basis
- Having the courage to give honest feedback so that his direct reports can learn and grow.
5. ENCOURAGE the Heart
- Relating to people more head-to-head and heart-to-heart.
- Adding fun to everyone’s work
- Infusing energy, hope, and joy into the lives of the people that you relate to.
- Talent Managers: Leaders need to work with their current employees to motivate, communicate and encourage them.
- Personalizing recognitions and making every celebration memorable.
- Making every relationship last for a lifetime.
6. Technology Proponent
Technology has not only enabled but also transformed HR performance. As a result, it has become increasingly important for HR professionals to be tech-savvy. Moreover, they must recognize the significant contributions that technology can make. In addition, they should actively propose and promote appropriate technology solutions. However, despite its importance, the competency domain of technology proponent is rated among the lowest in professional effectiveness.
Overall Findings
- Credible Activism is the highest-rated competency domain in every region
- Technology proponent and total rewards are the lowest rated competencies domain in every region
V. INDIA: HR COMPETENCIES AND COMPETITIVE PRACTICES
Review and Discussion of 2012 HRCS India Findings, Dave Ulrich et all 2013
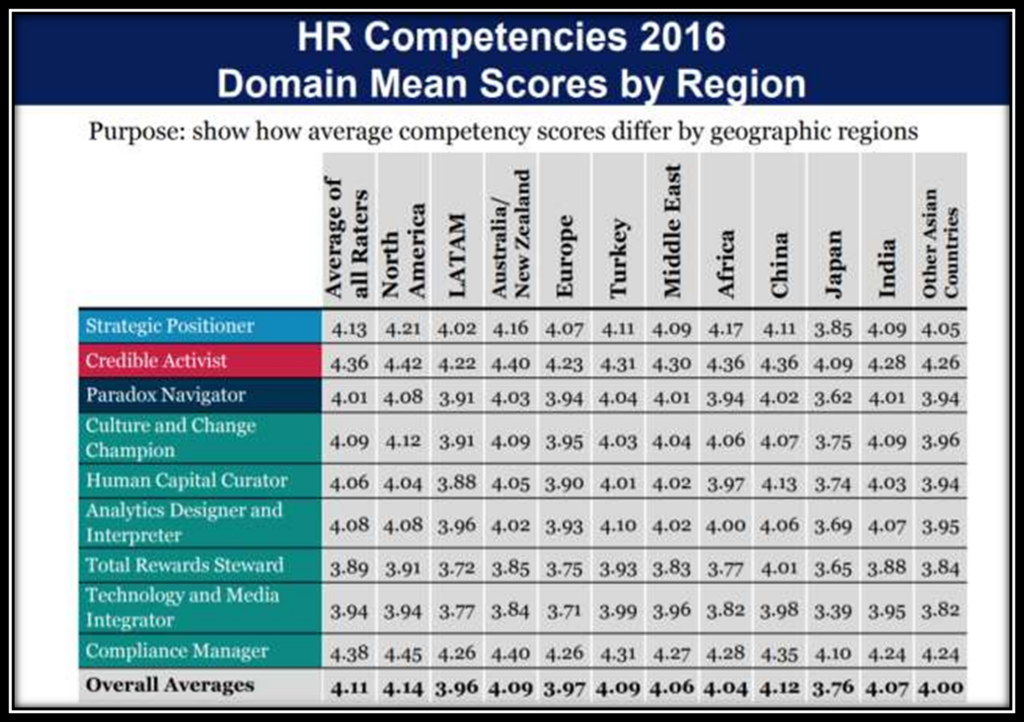
In this economic, governmental, and social context HR departments and line executives in India as elsewhere in the world have had to radically transform their vision and expectations of HR. Infosys spends US$ 65 on training for every US$1,000 in revenue; this compares to the US$6.17 spent by IBM. In 2012, 1,800 respondents participated in the HRCS survey in India/ The six competency domains have their own impact on individual and business performance in India.
1. Credible Activist
With an average score of 4.28, HR professionals in India are most adept in this domain. This provides a solid foundation for their involvement in other activities that are more centrally related to the business.
Coromandel International Ltd. Is a fertilizer, specially nutrients and crop protection company within the Murugappa Group. There was an intense discussion about the feasibility of keeping the Crop Protection manufacturing unit at a location that was being converted into a business office center.
According to HR Coromandel was convinced that the traditional well-accepted pattern of paying compensation and easing people out in this type of situation was not beneficial. HR introduced a program called “Go Kiss the World”, HR represented empirical research on the results of the traditional layoff schemes.
This study showed no matter how attractive the initial separation compensation after a few years vast majority of former employees were found to be in poor health, physically and financially. The company through this program sponsored employee trips to the new manufacturing locations.
As a result of Coromandel’s HR professionals striving to be credible activists, all stakeholders benefitted. Coromandel is now ranked by Business Today as one of the top 20 best companies to work for in India.
2. Capability Builder
HR professionals in India have reached a reasonably high level in the capability builder competency domain. In this context, Larsen & Toubro (L&T) stands out as a professionally managed company specializing in technology, engineering, construction, and manufacturing.
Furthermore, L&T has not only developed but also successfully sustained capabilities in technology and service solution development. In addition to this, its Framework for Linking Appraisals with Incentives and Rewards plays a crucial role in reinforcing these capabilities.
Moreover, this framework is seamlessly integrated with ICONS (Immense Contribution of Noteworthy Significance), a program dedicated to recognizing individual and team contributions. Consequently, L&T ensures that employees feel valued and motivated.
In addition, its succession planning process focuses on performance-based promotions, which, in turn, significantly enhances L&T’s organizational capability. As a result, the company continues to thrive in a highly competitive industry.
3. Change Champion
HR professionals in India confront the challenges of change at a high level of 4.09 out of 5.00. Excellent examples of HR professionals acting as change champions are found at HCL Technologies.
In 2005, the company line leadership together with senior HR professionals envisioned an organization that would recognize employees as primary value creators in the customer-employee relationship. The overall philosophy was called Employee First, Customer Second.
The responsibility and accountability were with the employee to create extraordinary levels of customer satisfaction and were facilitated by 360-degree evaluation. Best performers become members of 02 Club and they are honored with their families, and presented with trophies.
HR also instituted the Extra-Mile Program, which was modeled after airline frequent flier programs. Each employee receives 300 miles/year to give to others.
4. HR innovator and Integrator
Expeienced HR in India function as HR innovators and Integrators at a reasonably high level of 4.07 out of 5.00. HR Professionals at Bharti Airtel are effective examples of how to add value as HR innovators and Integrators. It is one
of the largest cellular service providers in India. In late 2000 HR professionals at Airtel clearly outlined a leadership competency framework that forms the bedrock of its people management systems. The “Jobs Never Done Before” initiative encourages Airtel’s employer brand position to be future-facing and customer-oriented and to “give scale to those who have entrepreneurial DNA, to charter to the unchartered”. A recognition process called Kudos creates online visibility and incentives for employees to demonstrate Airtel values and leadership competencies.
BleAp and ELeAP are programs for high-potential middle management through which they are groomed for business leadership roles which include classroom teaching, on-the-job training, special projects, and career movements spanning two to three years. As a result of these practices HR at Airtel is building unique winning capabilities for the business by constantly delivering trend-setting solutions to its business and people.
5. Strategic Positioner
HR professionals in India, hr function as strategic positioners at 4.09 out of 5.00. Dr. Reddy Laboratories is an exceptional example of a strategic positioner.
Dr. Reddy is an integrated global pharmaceutical company. It has more than US$ 2 billion threshold in annual revenues. Increasing competition, commoditization in generic markets, and pricing pressures are changing the business scenario for the pharmaceutical industry. So Dr. Reddy has revamped its business strategy with changing business needs.
- Alignment: Organization design, cross-business collaboration, harmonized practices, and employee engagement.
- Accountability: Performance metrics, robust reviews, and total rewards
- Ability: Talent management, Leadership development
6. Technology Proponent
In India HR Professionals are least skilled in this domain 3.95. Wipro Ltd. Is a significant example serving as role models of the technology proponent domain. In 2012, Wipro was ranked as India’s most valuable brand. Wipro HR has automated a wide range of transactions including payroll processing, taxation, employee data management, hiring and onboarding/ off-boarding and exits, salary and wage, incentives, performance management, leave and absence administration, time and attendance monitoring.
Wipro technology has changed the role of HR and redefined how employees can be enlisted to build solutions for businesses and customers alike.
(Dave Ulrich et all 2013, Global HR competencies)
VI. CONCLUSION
Future requirements of HR
Given the prospects of external change, we anticipate a future where human ingenuity and organization capability, as guided by the insightful line and HR leaders will emerge as the new frontier of competitive advantage.
Different global regions may take different paths to achieve competitive advantage but the agendas around talent, organization, and leadership are similar.
With emerging business conditions and HR granularity, we envision HR continuing to focus on the three demands; talent, organization, and leadership. The competitive challenge is to make the organization whole more productive than the sum of talented individuals.
Leaders are the charge of bringing talent and organization together.
VII. LEADERSHIP FUTURE TRENDS
Leaders have the dual responsibility of sourcing talent and creating organizational capabilities. As we contemplate leadership in the business context there are three trends:
1. From Command and Control to Coach, Collaborate and Communicate
Leaders get things done through others. In complex changing global organizations, leaders cannot govern by observing and telling others what to do. They have to get things done through the shared commitment to common goals. They need to enable others to act.
2. Why and What to How
Better leadership boosts customer share, productivity, and financial performance. Leadership in the future will increasingly attend to how leaders do what they know they should do. Leaders need to Model the way and challenge the process. It can be called leadership sustainability and believe that HR professionals should help leaders not only to figure out why and what they should do but also how to do it.
3. Leader to Leadership
Leaders are the specific individuals who direct work, often at the top of a company. Leadership exists all the way through the organization, in both domestic and global markets. Effective leaders work to optimize their teams and individuals within their teams; leadership seeks to integrate the entire hierarchy of leaders to optimize organization-wide performance.
(Dave Ulrich et all 2013, Global HR competencies)
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I am extremely grateful to Dr. Prashanta Kr. Panda, H.O.D. Economics, Central University of Tamil Nadu for numerous courtesies.
REFERENCES
- Leadership Challenge Work Book – by James M. Kouzes, Barry Z. Posner, June 2017
- Dave Ulrich, Norm Smallwood, Leadership Brand: Harvard Business School, Harvard Business School Press, 2007 – Business & Economics – 270 pages
- Madhavi Lakshmi, P., and P. Siva Pratap. “HR Analytics-a Strategic Approach to HR Effectiveness.” International Journal of Human Resource Management and Research (IJHRMR) ISSN (P) (2016): 2249-6874.
- Dave Ulrich, Wayne Brockbank, Jon Younger, Global HR Competencies -2013, Tata McGraw Hill Publication – 292 pages.
- Bajaj, P., and S. H. A. L. I. N. I. Sinha. “Successful human resource management determinants to build good employee relations: A quantitative approach.” International Journal of Human Resource Management and Research (IJHRMR) 3.2 (2013): 31-36.
- Annjaan Daash, Tomorrows competencies of marketing agents, Pezzottaite Journals, March 2013, Vol 2,
No. 1, Pg 172-177
- Suchitra, P. “E-HRM: conceptual implications.” International Journal of Human Resource 4.2 (2014): 31- 38.
- Annjaan Daash et all, Competency Mapping of Marketing Agents Epra International Journal, Vol. 7, May 2019, Pg 5-11
- Prajapati, M., Ritambhara Singh, and DilipVahoniya. “A Study on Conceptual Framework of Human Resource Accounting in India.” International Journal of Human Resource Management and Research (IJHRMR) 6.3 (2016): 7-12.
- Annjaan Daash, Tomorrow competencies for customer focussed leaders, Shiv Shakti International Journal, Dec 2013, Vol 1, No. 4
- Sulphey, M. M. “The utility of Q-methodology in Human Resource Management research.” International Journal of Human Resources Management 3.3 (2014): 15-26.
- Annjaan Daash et all, Competency-based training design: focus on Leadership, Icfai Business School May
2019, Pg 12-18
- Vohra, P. S., and Vipula Chaudhary. “Human Resource Accounting Practices Leads Firms Performance.” International Journal of Business and General Management (IJBGM) ISSN (P) (2014): 2319-2267.



















